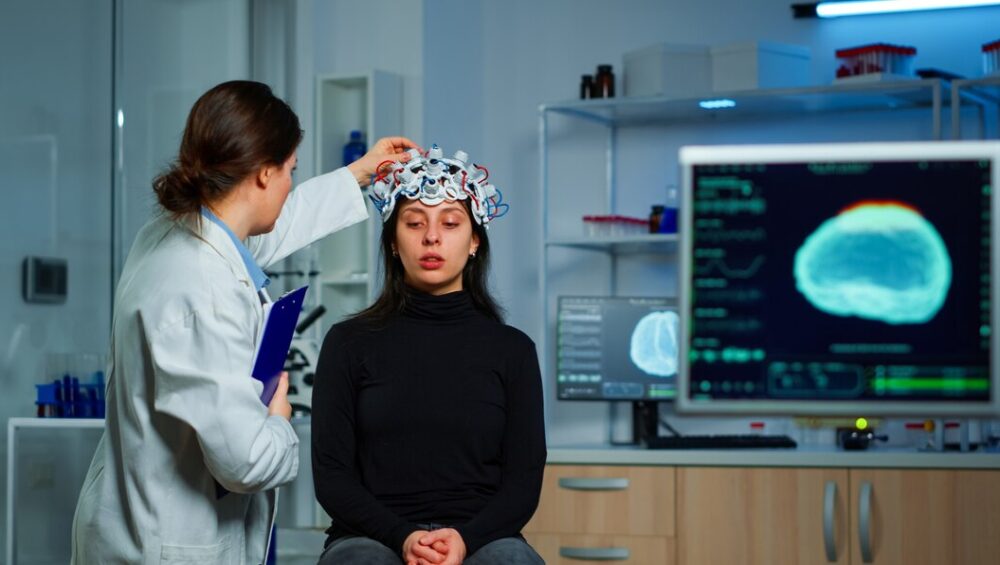
Introduction
Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) refers to damage to the brain that occurs after birth due to trauma, stroke, illness, or other medical conditions. This condition can affect a person’s ability to move, communicate, think, and interact with others. Understanding ABI, its causes, symptoms, and available support services is essential for ensuring that individuals with ABI receive the care and assistance they need.
At Careable , we specialize in providing personalized NDIS support services for individuals with ABI. Our tailored programs assist with daily living, community participation, therapy coordination, and Supported Independent Living (SIL) . Whether helping with mobility, therapy sessions, or social engagement , our goal is to empower individuals with ABI to lead independent and fulfilling lives .
Causes of Acquired Brain Injury
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) – Caused by external forces such as falls, car accidents, or assaults.
- Stroke – A disruption of blood flow to the brain, leading to damage.
- Brain Tumors – Growths that can compress and damage brain tissue.
- Infections – Meningitis, encephalitis, and other infections affecting the brain.
- Lack of Oxygen (Anoxia/Hypoxia) – Caused by drowning, heart attacks, or carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Substance Abuse – Alcohol or drug-related brain damage.
- Neurological Diseases – Conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease.
Symptoms and Effects of ABI
Cognitive Symptoms
- Memory loss or difficulty retaining new information.
- Reduced attention span and difficulty concentrating.
- Impaired problem-solving and decision-making abilities.
- Difficulty with language and communication (aphasia).
Physical Symptoms
- Muscle weakness, paralysis, or coordination difficulties.
- Chronic headaches and dizziness.
- Seizures or epilepsy following a brain injury.
- Fatigue and difficulty with balance or motor skills.
Emotional & Behavioral Changes
- Mood swings, depression, and anxiety.
- Difficulty controlling emotions (emotional lability).
- Impulsive or inappropriate behavior.
- Changes in personality and social interactions.
Treatment and Rehabilitation for ABI
- Physical Therapy – Helps regain motor function, coordination, and muscle strength.
- Occupational Therapy – Assists in relearning daily activities like dressing, cooking, and personal care.
- Speech Therapy – Supports individuals with speech, communication, and swallowing difficulties.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation – Focuses on improving memory, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Psychological Counseling – Addresses emotional and behavioral changes through therapy and support groups.
- Medication – Used to manage symptoms like seizures, mood disorders, and pain.
- Assistive Technology – Devices such as voice recognition software and mobility aids enhance independence.
How Careable Supports Individuals with Physical Disabilities
At Careable, we believe in empowering individuals with physical disabilities by providing comprehensive NDIS-funded services tailored to their unique needs. Our team works closely with participants and their families to ensure they receive the best care, therapy, and assistive solutions.
✅ Assistance with Daily Living (ADL)
✅ Supported Independent Living (SIL)
✅ Assistive Technology Support
Conclusion
Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) can significantly impact a person’s life, but with the right support, individuals can regain independence and thrive. At Careable , we are passionate about providing NDIS-funded services that empower individuals with ABI to achieve their goals. Whether it’s daily support, therapy coordination, or community inclusion , we are here to help.
📞 Contact Us
If you or a loved one needs NDIS-funded support for ABI , reach out to our team today.
📞 Call us: 1300 DECIDE
📩 Email us: cx@careable.com.au
🌐 Visit us: [www.careable.com.au]
FAQs
What is the difference between ABI and TBI?
TBI is a type of ABI caused by external trauma, such as falls or accidents, while ABI includes non-traumatic causes like stroke and infections.
Can someone recover fully from an ABI?
Recovery depends on the severity and location of the injury. Some individuals regain full function, while others may require lifelong support and adaptations.
How does ABI affect daily life?
ABI can impact mobility, communication, cognitive functions, and emotional well-being, making daily tasks more challenging and requiring adaptations.
What NDIS services are available for ABI support?
NDIS provides funding for therapy, assistive technology, community participation, and supported living services. Careable offers personalized NDIS-funded programs to help individuals with ABI regain independence.
How can I apply for NDIS support for ABI?
You can apply through the NDIS website or contact 1300 DECIDE for assistance in navigating the process.